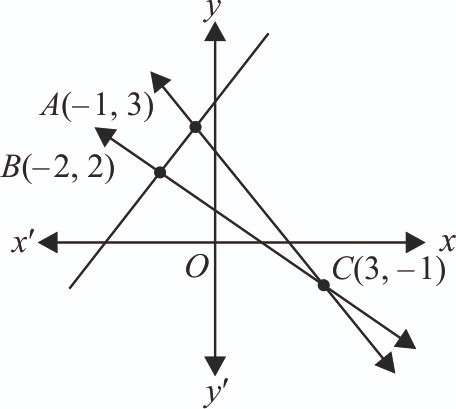
The vertices of a triangle are A(–1, 3), B(–2, 2) and C(3, –1). A new triangle is formed by shifting the sides of the triangle by one unit inwards. Then the equation of the side of the new triangle nearest to origin is [2024]
(4)
Equation of AC :
Equation AB :
Equation BC :
Distance of AC from origin O(0, 0) =
Distance of AB from origin O(0, 0) =
Distance of BC from origin O(0, 0) =
When each side of shifted by one unit inwards distance of new sides from origin are respectively.
Clearly new position of AC is nearest to the origin.
Equation of AC when shifted by one unit inwareds can be chosen as x + y = c
Thus, we have
Required equation is .
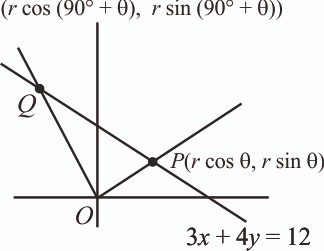
Let two straight lines drawn from the origin O intersect the line 3x + 4y = 12 at the points P and Q such that is an isosceles triangle and . If , then the greatest integer less than or equal to is: [2024]
44
42
46
48
(3)
Let and
Now, in
Now,
P and Q lies on 3x + 4y = 12
... (i)
and
... (ii)
From (i) and (ii), we have
Now,
So, .
Let A(–1, 1) and B(2, 3) be two points and P be a variable point above the line AB such that the area of is 10. If the locus of P is ax + by = 15, then 5a + 2b is: [2024]
6
4
(4)
Let coordinates of P be (h, k).
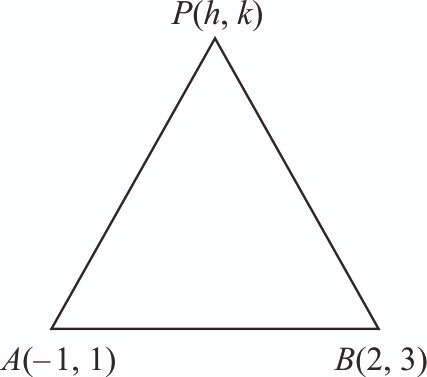
Area of = 10sq. units
( P is above the line AB, so we take only +ve value)
On comparing it with ax + by = 15, we get and
.
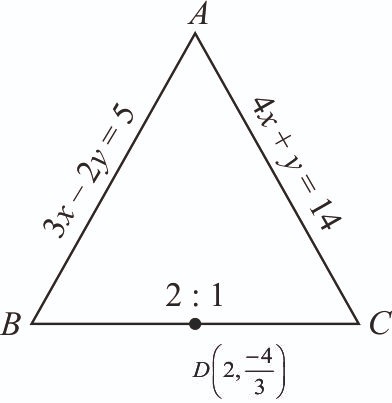
The equations of two sides AB and AC of a triangle ABC are 4x + y = 14 and 3x – 2y = 5, respectively. The point divides the third side BC internally in the ratio 2 : 1, the equation of the side BC is [2024]
x + 3y + 2 = 0
x – 3y – 6 = 0
x + 6y + 6 = 0
x – 6y – 10 = 0
(1)
Let be the point on BC which divides BC in ratio 2 : 1.
Let coordinates of B be and coordinates of C be
Now, ,
On solving these two equations, we get,
So B(4, –2) and C(1, –1) are the required points.
Equation of BC :
The Portion of the line 4x + 5y = 20 in the first quadrant is trisected by the lines and passing through the origin. The tangent of an angle between the lines and is: [2024]
(1)
Lines and trisect the line 4x + 5y = 20.
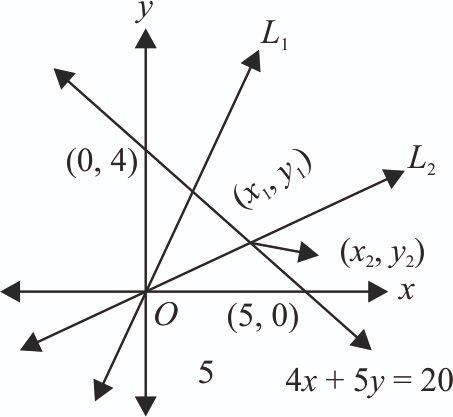
Similarly,
Slope of line
Slope of line
Tangent angle between the lines and :
Let R be the interior region between the lines 3x – y + 1 = 0 and x + 2y – 5 = 0 containing the origin. The set of all values of a, for which the points lie in R, is: [2024]
(4)
It is given that, region R lies between the lines 3x – y + 1 = 0 and x + 2y – 5 = 0.
The point and (0, 0) lie in the region R.
and (0, 0) are on same side of both the line.
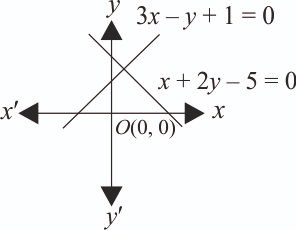
For Line 3x – y + 1 = 0, O(0, 0) is on the right side of the line.
So, point will also be on right side of the line.
... (i)
For line x + 2y – 5 = 0, O(0, 0) is on the left side of the line.
So, point will also be on left side of the line.
... (ii)
From the intersection of (i) and (ii), we get
In a , Suppose y = x is the equation of the bisector of the angle B and the equation of the side AC is 2x – y = 2. If 2AB = BC and the points A and B are respectively (4, 6) and , then is equal to [2024]
39
42
48
45
(2)
We have, y = x ... (i)
and 2x – y = 2 ... (ii)
Solving (i) and (ii), we get x = 2 and y = 2
As,
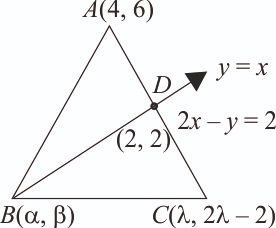
The image of the point A will lies on the line BC.
Let A' = (6, 4)
Now,
The distance of the point (2, 3) from the line 2x – 3y + 28 = 0, measured parallel to the line , is equal to [2024]
(1)
Slope of a line passing through (2, 3) and parallel to line is same as that of line
So, slope of line =
So, equation of line passing through (2, 3) and having slope in normal form is,
This line passes through 2x – 3y + 28 = 0
Let A be the point of intersection of the lines 3x + 2y = 14, 5x – y = 6 and B be the point of intersection of the lines 4x + 3y = 8, 6x + y = 5. The distance of the point P(5, –2) from the line AB is [2024]
8
6
(4)
Point of intersection of lines 3x + 2y = 14 and 5x – y = 6 is A(2, 4)
Point of intersection of lines 4x + 3y = 8 and 6x + y = 5 is
So, equation of line AB is,
Distance of point P(5, –2) from 4x – 3y + 4 is given as
A line passing through the point A(9, 0) makes an angle of 30° with the positive direction of x-axis. If this line is rotated about A through an angle of 15° in the clockwise direction, then its equations in the new position is [2024]
(2)
Let be the line passing through point A(9, 0) making angle 30° with x-axis.
Line is rotated clockwise by 15° then is the new position of line where it make 15° angle with x-axis.
So, equation of line passing through (9, 0) and making angle 15° with x-axis is (y – 0) = tan 15° (x – 9)
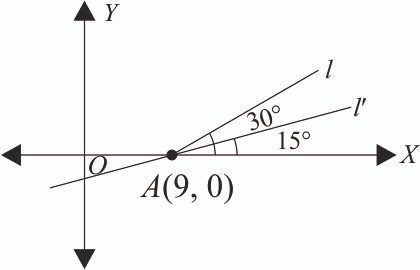
y = tan (45° – 30°)(x – 9) =