What happens to freezing point of benzene when small quantity of naphthalene is added to benzene? [2024]
Increases
Remains unchanged
First decreases and then increases
Decreases
(4)
When a small quantity of naphthalene is added to benzene its freezing point decreases.
The osmotic pressure of a dilute solution is Pa at 273 K. Osmotic pressure of the same solution at 283 K is _______ . [2024]
(73)
Mass of ethylene glycol (antifreeze) to be added to 18.6 kg of water to protect the freezing point at -24°C is _____ kg.
(Molar mass in g for ethylene glycol 62, of water = 1.86 K kg ) [2024]
(15)
2.5 g of a non-volatile, non-electrolyte is dissolved in 100 g of water at 25°C. The solution showed a boiling point elevation by 2°C. Assuming the solute concentration in negligible with respect to the solvent concentration, the vapour pressure of the resulting aqueous solution is ____ mm of Hg (nearest integer).
[Given: Molal boiling point elevation constant of water ,1 atm pressure = 760 mm of Hg, Molar mass of water = 18 g ] [2024]
(711)
By Raoult's law:
Note: is not given in question, question is solved by taking it as 760 mmHg which is not correct as 760 mmHg is vapor pressure of water at but temperature in question is .
2.7 Kg of each of water and acetic acid are mixed. The freezing point of the solution will be °C. Consider the acetic acid does not dimerise in water, nor dissociates in water. = _______ (nearest integer)
[Given: Molar mass of water = 18 g , acetic acid = 60 g
] [2024]
(31)
As water is in excess, it is solvent.
An artificial cell is made by encapsulating 0.2 M glucose solution within a semipermeable membrane. The osmotic pressure developed when the artificial cell is placed within a 0.05 M solution of NaCl at 300 K is ______ bar. (Nearest Integer)
[Given: R = 0.083 L bar ]
Assume complete dissociation of NaCl [2024]
(25)
Osmotic pressure developed = Difference of osmotic pressure due to glucose solution difference of osmotic pressure due to NaCl solution.
Considering acetic acid dissociates in water, its dissociation constant is . If 5 mL of acetic acid is dissolved in 1 litre water, the solution will freeze at °C, provided pure water freezes at 0 °C. = ________ .(Nearest integer)
Given: = 1.86 K kg .
density of acetic acid is 1.2 g .
molar mass of water = 18 g .
molar mass of acetic acid = 60 g .
density of water = 1 g
Acetic acid dissociates as
[2024]
(19)
Consider the dissociation of the weak acid HX as given below:
[: dissociation constant]
The osmotic pressure of 0.03 M aqueous solution of HX at 300 K is ______ bar (nearest integer).
[Given: R = 0.083 L bar ] [2024]
(76)
0.05M when treated with 0.01M gives green colour solution of . The two solutions are separated as shown below:
[SPM: Semi Permeable Membrane]

Due to osmosis: [2024]
Green colour formation observed on side X.
Molarity of solution is lowered.
Green colour formation observed on side Y.
Molarity of solution is lowered.
(4)

Solute particles do not move across SPM, so reaction between and does not occur and green colour formation does not occur in either chamber. Net movement of solvent is from hypotonic (side X) to hypertonic (side Y) solution. Hence molarity of solution decreases.
When mL methanol (molar mass = 32 g; density = 0.792 ) is added to 100 mL water (density = 1 ), the following diagram is obtained.
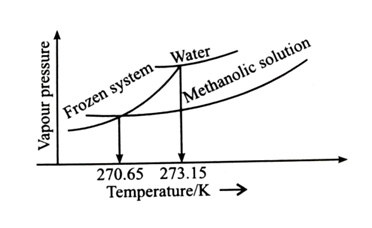
x = ___________ (nearest integer)
[Given: Molal freezing point depression constant of water at 273.15 K is 1.86 K kg ] [2024]
(543)