Match List I with List II. [2024]
| List I | List II | ||
| A. | Down’s syndrome | I. | 11?? chromosome |
| B. | -Thalassemia | II. | ‘X’ chromosome |
| C. | -Thalassemia | III. | 21?? chromosome |
| D. | Klinefelter’s syndrome | IV. | 16?? chromosome |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
In which disorder change of single base pair in the gene for beta globin chain results in change of glutamic acid to valine? [2023]
Thalassemia
Sickle cell anemia
Haemophilia
Phenylketonuria
(2)
Sickle cell anemia is caused by the substitution of Glutamic acid (Glu) by Valine (Val) at the sixth position of the beta globin chain of the haemoglobin molecule. The substitution of amino acid in the globin protein results due to the single base substitution at the sixth codon of the beta globin gene from GAG to GUG.
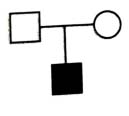
Which one of the following symbols represents mating between relatives in human pedigree analysis? [2023]

(4)
In pedigree analysis,  symbol shows consanguineous mating, i.e., mating between relatives.
symbol shows consanguineous mating, i.e., mating between relatives.
Which of the following statements are correct about Klinefelter’s Syndrome? [2023]
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866).
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine development is also expressed.
C. The affected individual is short statured.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
E. Such individuals are sterile.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
B and E only
A and E only
A and B only
C and D only
(1)
Klinefelter’s syndrome is a genetic disorder caused due to the presence of an additional copy of X-chromosome resulting into a karyotype of 47, XXY. Such an individual has overall masculine development, however the feminine development (development of breast i.e., gynaecomastia) is also expressed. Such individuals are sterile.
Broad palm with single palm crease is visible in a person suffering from [2023]
Klinefelter’s syndrome
Thalassemia
Down’s syndrome
Turner’s syndrome
(3)
Broad palm with characteristic palm crease, small round head, furrowed tongue and retarded mental development are characteristics of Down’s syndrome. It is a genetic disorder due to the presence of an additional copy of chromosome number 21 (trisomy of 21).
Select the correct match. [2020]
Haemophilia – Y linked
Phenylketonuria – Autosomal dominant trait
Sickle cell anaemia – Autosomal recessive trait, chromosome -11
Thalassemia – X linked
What is the genetic disorder in which an individual has an overall masculine development, gynaecomastia and is sterile? [2019]
Down’s syndrome
Turner’s syndrome
Klinefelter’s syndrome
Edward syndrome
(3)
Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs by the union of an abnormal XX egg and a normal Y sperm or a normal X egg and abnormal XY sperm. The individual has 47 chromosomes (44 + XXY). Such persons are sterile males with undeveloped testes, mental retardation, sparse body hair, long limbs and with some female characteristics such as enlarged breast, i.e., gynaecomastia.
A woman has an X-linked condition on one of her X chromosomes. This chromosome can be inherited by [2018]
only daughters
only sons
only grandchildren
both sons and daughters
(4)
Woman acts as a carrier when she has the X-linked condition on one of her X-chromosomes. Both son and daughter inherit X-chromosome from mother. Hence, one of the two daughters will be carrier and one of the two sons will be diseased. It can be explained by the given cross:
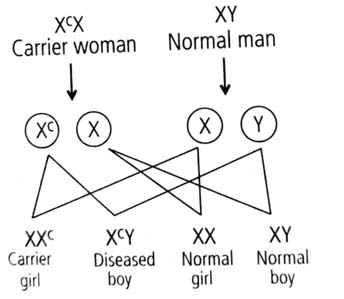
where is the X-chromosome carrying the gene for the condition.
Thalassemia and sickle cell anaemia are caused due to a problem in globin molecule synthesis. Select the correct statement. [2017]
Both are due to a quantitative defect in globin chain synthesis.
Thalassemia is due to less synthesis of globin molecules.
Sickle cell anaemia is due to a quantitative problem of globin molecules.
Both are due to a qualitative defect in globin chain synthesis.
(2)
Sickle cell anaemia is caused due to point mutation in which at the 6th position of beta globin chain, glutamic acid is replaced by valine. Thus, it is a qualitative defect in functioning of globin molecules.
Thalassemia is caused due to either mutation or deletion which ultimately results in reduced rate of synthesis of one of the globin chains that make up haemoglobin. Hence, it is a quantitative defect in functioning of globin molecules.
A disease caused by an autosomal primary non-disjunction is [2017]
Klinefelter’s syndrome
Turner’s syndrome
Sickle cell anaemia
Down’s syndrome
(4)
Down’s syndrome is an autosomal aneuploidy, caused by the presence of an extra-chromosome number 21. Both the chromosomes of the pair 21 pass into a single egg due to non disjunction during oogenesis.