CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
| Unit No | UNIT | MARKS |
| I | Chemical Substances-Nature and Behaviour | 25 |
| II | World of Living | 25 |
| III | Natural Phenomena | 12 |
| IV | Effects of Current | 13 |
| V | Natural Resources | 05 |
| Total | 80 | |
| Internal assessment | 20 | |
| Grand Total | 100 |
Theme: Materials
Unit I: Chemical Substances - Nature and Behaviour
Chemical reactions: Chemical equation, Balanced chemical equation, implications of a balanced chemical equation, types of chemical reactions: combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, precipitation, endothermic exothermic reactions, oxidation and reduction.
Acids, bases and salts: Their definitions in terms of furnishing of H+ and OH– ions, General properties, examples and uses, neutralization, concept of pH scale (Definition relating to logarithm not required), importance of pH in everyday life; preparation and uses of Sodium Hydroxide, Bleaching powder, Baking soda, Washing soda and Plaster of Paris.
Metals and nonmetals: Properties of metals and non-metals; Reactivity series; Formation and properties of ionic compounds; Basic metallurgical processes; Corrosion and its prevention.
Carbon compounds: Covalent bonding in carbon compounds. Versatile nature of carbon. Homologous series. Nomenclature of carbon compounds containing functional groups (halogens, alcohol, ketones, aldehydes, alkanes and alkynes), difference between saturated hydro carbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chemical properties of carbon compounds (combustion, oxidation, addition and substitution reaction). Ethanol and Ethanoic acid (only properties and uses), soaps and detergents.
Theme: The World of the Living
Unit II: World of Living
Life processes: ‘Living Being’. Basic concept of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals.
Control and co-ordination in animals and plants: Tropic movements in plants; Introduction of plant hormones; Control and co-ordination in animals: Nervous system; Voluntary, involuntary and reflex action; Chemical co-ordination: animal hormones.
Reproduction: Reproduction in animals and plants (asexual and sexual) reproductive health - need and methods of family planning. Safe sex vs HIV/AIDS. Child bearing and women’s health.
Heredity and Evolution: Heredity; Mendel’s contribution- Laws for inheritance of traits: Sex determination: brief introduction: (topics excluded - evolution; evolution and classification and evolution should not be equated with progress).
Theme: Natural Phenomena
Unit III: Natural Phenomena
Reflection of light by curved surfaces; Images formed by spherical mirrors, centre of curvature, principal axis, principal focus, focal length, mirror formula (Derivation not required), magnification.
Refraction; Laws of refraction, refractive index.
Refraction of light by spherical lens; Image formed by spherical lenses; Lens formula(Derivation not required); Magnification. Power of a lens.
Functioning of a lens in human eye, defects of vision and their corrections, applications of spherical mirrors and lenses.
Refraction of light through a prism, dispersion of light, scattering of light, applications in dailylife (excluding colour of the sun at sunrise and sunset).
Theme: How Things Work
Unit IV: Effects of Current
Electric current, potential difference and electric current. Ohm’s law; Resistance, Resistivity, Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends. Series combination of resistors, parallel combination of resistors and its applications in daily life. Heating effect of electric current and its applications in daily life. Electric power, Interrelation between P, V, I and R. Magnetic effects of current : Magnetic field, field lines, field due to a current carryingconductor, field due to current carrying coil or solenoid; Force on current carrying conductor, Fleming’s Left Hand Rule, Direct current. Alternating current: frequency of AC. Advantage of AC over DC. Domestic electric circuits.
Theme: Natural Resources
Unit V: Natural Resources
Our environment: Eco-system, Environmental problems, Ozone depletion, waste production and their solutions. Biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
Note for the Teachers:
The chapter Management of Natural Resources (NCERT Chapter 16) will not be assessed in the year-end examination. However, learners may be assigned to read this chapter and encouraged to prepare a brief write up to any concept of this chapter in their Portfolio. This may be for Internal Assessment and credit may be given Periodic Assessment/Portfolio).
The NCERT text books present information in boxes across the book. These help students to get conceptual clarity. However, the information in these boxes would not be assessed in the year-end examination.
COURSE STRUCTURE CLASS – X
The NCERT text books present information in boxes across the book. These help students to get conceptual clarity. However, the information in these boxes would not be assessed in the year-end examination.
|
Units |
Unit Name |
Marks |
| I | NUMBER SYSTEMS | 06 |
| II | ALGEBRA | 20 |
| III | COORDINATE GEOMETRY | 06 |
| IV | GEOMETRY | 15 |
| V | TRIGONOMETRY | 12 |
| VI | MENSURATION | 10 |
| VII | STATISTICS & PROBABILITY | 11 |
| Total | 80 |
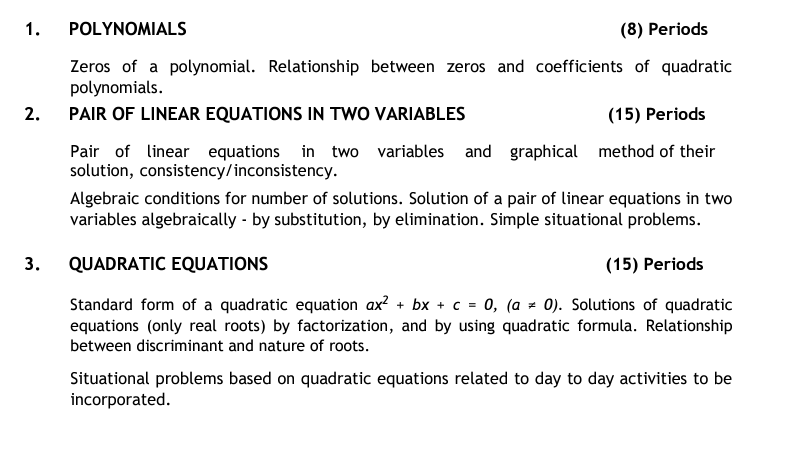
UNIT I: NUMBER SYSTEMS
1. REAL NUMBER
ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS
Motivation for studying Arithmetic Progression Derivation of the nth term and sum of the first n terms of A.P. and their application in solving daily life problems.
UNIT III: COORDINATE GEOMETRY
Coordinate Geometry
Review: Concepts of coordinate geometry, graphs of linear equations. Distance formula. Section formula (internal division).
UNIT IV: GEOMETRY
TRIANGLES
Definitions, examples, counter examples of similar triangles.
1. (Prove) If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
2. (Motivate) If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel to the third side.
3. (Motivate) If in two triangles, the corresponding angles are equal, their corresponding sides are proportional and the triangles are similar.
4. (Motivate) If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, their corresponding angles are equal and the two triangles are similar.
5. (Motivate) If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides including these angles are proportional, the two triangles are similar.
CIRCLES
Tangent to a circle at, point of contact
1. (Prove) The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
2. (Prove) The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.

CBSE Class 10 Syllabus Maths - Download
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus Science - Download
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus Social Science - Download
CBSE Class 9 Syllabus Maths - Download
CBSE Class 9 Syllabus Science - Download
CBSE Class 9 Syllabus Social Science - Download
Smartachivers
Jan 07,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 07,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 06,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 06,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 05,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 04,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 04,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 02,2025
Smartachivers
Jan 02,2025
Smartachivers
Dec 31,2024
Smartachivers
Dec 31,2024
Smartachivers
Dec 30,2024
Smartachivers
Dec 30,2024